In order to setup email encryption, you’ll need to import a personal email certificate. If you don’t already have one, you can get a free certificate from Comodo. The certificate must be in .p12 or .pfx format.
Importing your personal certificate
Start by logging into Backstage webmail. Open the dropdown menu by clicking on your name, and go to Settings. From there, select Secure Messages from the list on the left.
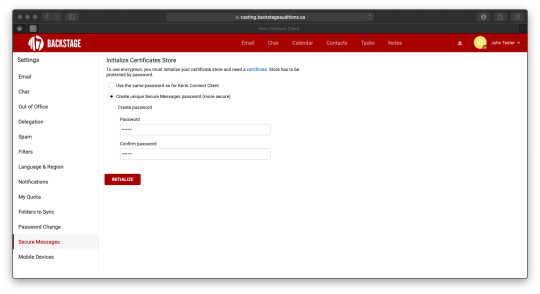
Select Create unique Secure Messages password (more secure) and enter a password. This password is will be required any time you want to access your certificate store (i.e. to add a certificate, or to use the certificate from another device/email client). Click on Initialize.
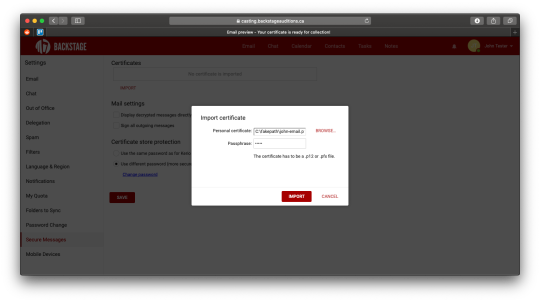
Now you’ll have the option to Import a certificate. Browse for the .p12 or .pfx file on your system, and enter the passphrase used to protect it. For security purposes, webmail will always display the path to your certificate file as “C:fakepath”. Click on Import to upload the certificate.
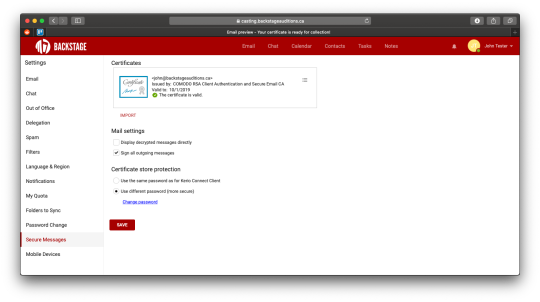
Note the options under Mail settings:
Display encrypted messages directly – automatically displays the contents of an encrypted message. When disabled, webmail will indicate that a message is encrypted and requires you to click a Display button in order to read it.
Sign all outgoing messages – automatically signs all outgoing emails with your certificate’s public key.
Signing and encrypting emails
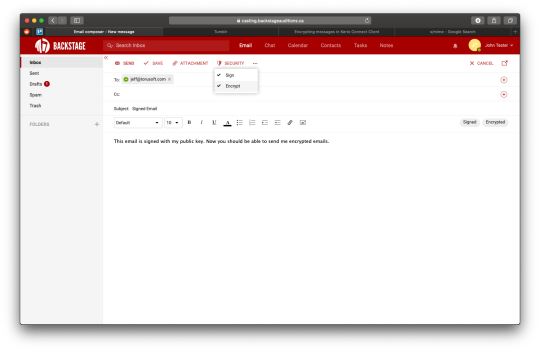
Now that your’ve added set up your certificate(s), you’ll be able to click on Security when composing an email, and select the following:
Sign – Digitally signs the message using your certificate’s public key. By doing this, the recipient will get your public key and can use it to send you encrypted messages.
Encrypt – Encrypts the message using the recipient’s public key. By doing this, only the intended recipient can view the contents of the message because only they posses the private key required to decrypt it.
NOTE: You cannot send an encrypted message to someone unless you have their public key. Webmail automatically stores the public key for another person’s email address when you receive a signed message from them.